Class Hours: 10:05 – 2:40
Mr. Bohmann | wbohmann@ewsd.org
10:05 Today’s Notes & Attendance
- Lunch Order – for Friday CCV
- National Technical Honor Society – Review Poster
- Call Backs: Sylvie – 1pm.
10:10 Scrum Meeting

Let’s talk about where we are at…
10:15 Aperture and Shutter Priority in Photography
Aperture Priority mode, you have control over the Focal Length which is referred to as the lense field of view. Cheat Sheet
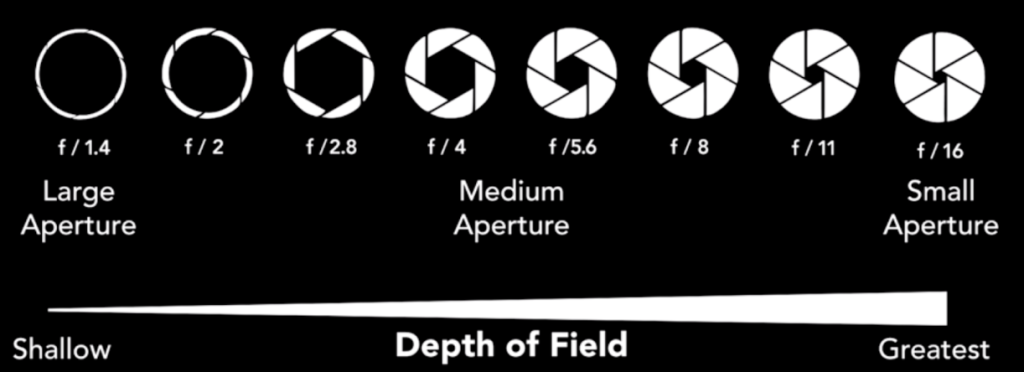
A small f-stop number (f2) means a small depth of field and large f-stop number (f22) means a large depth of field. From our activity yesterday a nice blurry background is more pronounced when we have our primary subject close and it fills the frame.
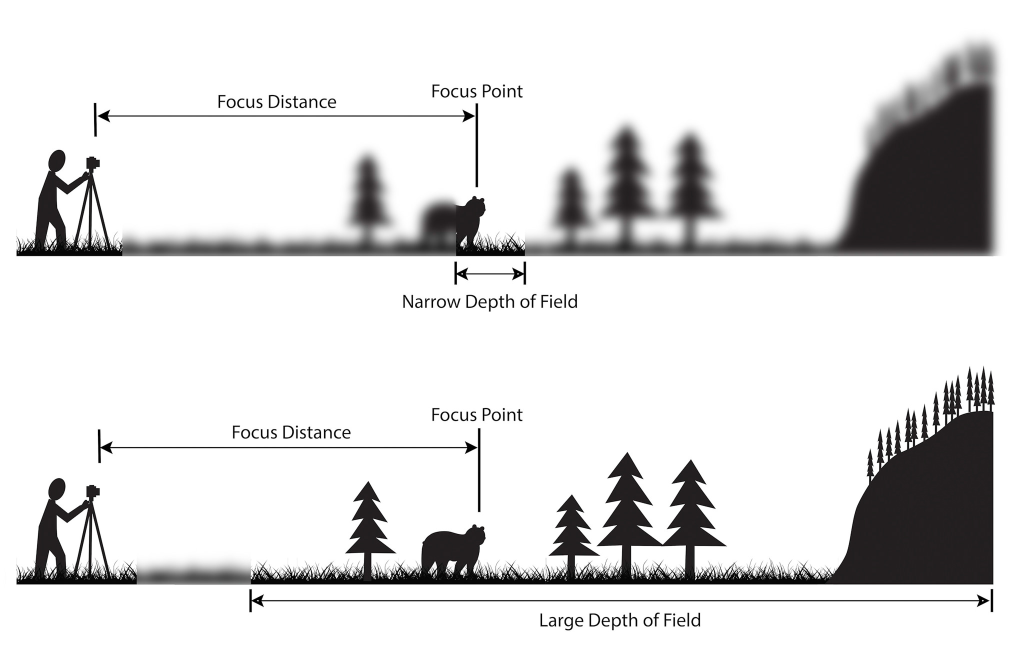
large f/stop numbers create a deep depth of field as seen in the second image
10:25 Shutter Priority (Tv)

Link to Photography Terms & Concepts
Shutter Priority mode allows you as the photographer to take charge of the speed of the shutter. To review, when you press the button to take a picture, the photo become exposed and the shutter closes when the exposure is complete.
The photo above is a classic example of motion blur using Shutter Priority mode.
The slower the shutter speed the more light is received by the image sensor.
The faster the shutter speed, the less light hits the sensor.
Let’s brainstorm some reasons why we would want to try shooting in Shutter Priority…

A really good way to get an understanding of focal length, depth of field and f/stops is to set up a model in Blender and play with all the the camera settings to see how things work.
While we are at it, we can also play with shutter speed!
Blender’s camera is not like our real camera. The Blender camera is a simulation. That means that Shutter speed is not part of the actual camera in Blender. Rather, shutter speed is part of Motion Blur which is found in the render settings. Let’s continue with our model…

Some settings in Motion Blur to consider (in Blender):
Position:
- Center middle frames of animation
- Start frames of animation
- End frames of animation
Shutter:
- .01 is one hundredth of a second
- .5 is a half second
- 1 is one second
10:50 Morning Break (10 minutes)
11:00 Fundamental Programming with C# & Unity

Each Wednesday we’ll do a little programming to get more familiar with the Unity interface and help each of you get more comfortable with game programming. This practice will translate well when we get to SkillsUSA work and our full game unit next semester. I promise to keep the coding manageable!
Last week we looked at variables – specifically int which are whole numbers, float which are decimals and string which are for words, phrases etc…
We also learned that variable scope refers to where you place your variables. If you placed your variable in the Start method, it will run when the game begins and then not be accessible again. If you place your variables at the top of your code, they are available across methods and functions.
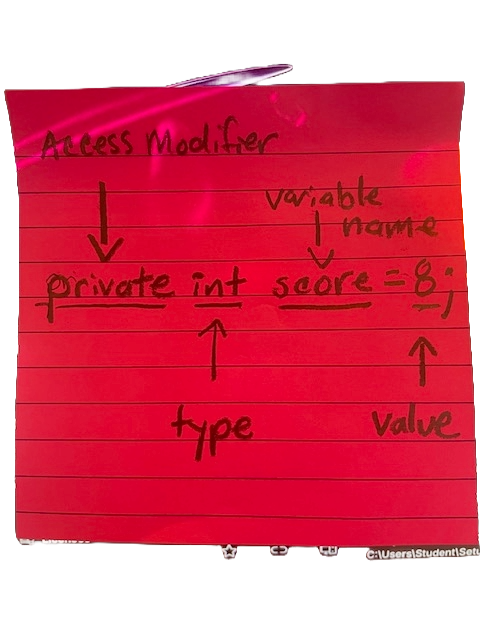
Public variables are accessible from game play and from other scripts. Private variables, which is the default for variables are available only for that script.
[SerializeField] is a private variable type but is available from game play to adjust while testing
Check out all the variables in the gameboard above!
public class MyScript : MonoBehaviour {
int score; // declare an int called Score
float currentDirection; // declare the float currentDirection
char myInitial; // declare a char called myInitial
string userName; // declare a string called userName
bool isMoving; // declare a bool called isMoving
void Start () {
// numeric data types do not require quotes
score = 8;
// use the "F" suffix to specify a float value
currentDirection = 90.2F;
// use single quotes around individual characters
myInitial = 'A';
// use double quotes around groups of characters
userName = "Will Bohmann";
// boolean values are either true or false
isMoving = true;
}
}
We already know that we use variables to provide more code flexibility. In many cases we may want to store mathematical operations in a variable. Let’s look at some common math operations.
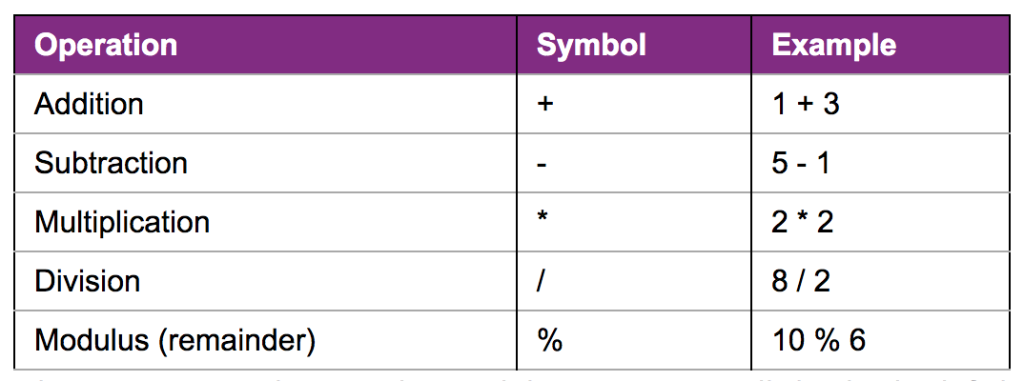
int added = 3 + 4; // added is 7
int subtracted = 3 - 4; // subtracted is -1
int multiplied = 3 * 4; // multiplied is 12
int divided = 12 / 4; // divided is 3
int remainder = 12 % 5; // remainder is 211:35 Lunch
12:05 Working in Shutter Priority
In class we’ll look at your camera settings for shooting in Shutter Priority mode.
Big Questions?
- How does light impact your images when shooting in Shutter Priority?
- How can you eliminate camera shake?
- What is the exposure triangle? For that matter, what is exposure?
Activity: Using Shutter Priority and with a partner, Capture:
- Partner running – freeze action
- Partner running – blur action
- Partner jump – freeze action
- Partner jump – blur action
- Close Up of flower with slow shutter speed
- Close Up of flower with fast shutter speed
- Slow shutter camera swirl
Return to the classroom, import and review. Practice using Adobe Bridge to review your shots and to do some editing with Camera Raw or Photoshop.
Before Production, post your favorite shot of the bunch… Be prepared to say why
12:35 Independent Production & Guided Support
These are your current Assignments:
- Next round of Sweatshirt designs – One Original and Digital – Due Thursday
- 6 Pack Personal Logos (paper designs) – Due Today
- Color Isolation Assignment – Due Today
- Featured Element Photography Assignment – Due Wednesday, September 24th
1:00 Afternoon Break

1:15 Dailies

1:20 Independent Reading

1:45 Dismissal

